Our Products Cannot Be Used As Medicines Directly For Personal Use.


Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Hydrolases
Hydrolases are a large and diverse class of enzymes that play a fundamental role in the biochemistry of living organisms. These enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of chemical bonds, a process in which a water molecule is used to break down substrates into simpler components. Hydrolases are involved in a variety of biological processes, including digestion, metabolism, signal transduction and regulation of cellular activities. Because of their versatility and ubiquity, hydrolases are extensively studied and used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food production, and environmental management. Creative Enzymes offers over 1000 types of hydrolases, explore our full product list and learn more about hydrolases with us!
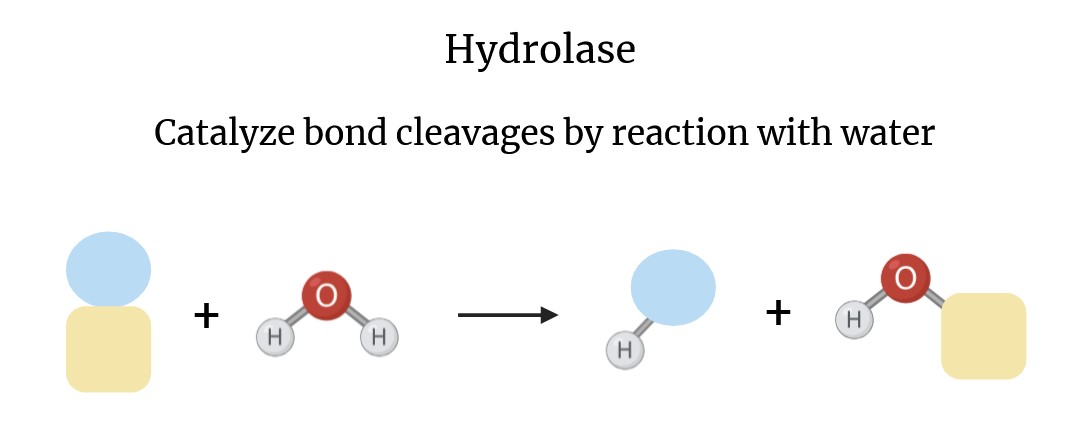
Hydrolases are classified under the EC (Enzyme Commission) number 3, which designates them as enzymes that catalyze hydrolysis reactions. These enzymes act on a variety of chemical bonds, including ester, glycosidic, peptide, and phosphodiester bonds. The general reaction catalyzed by hydrolases can be represented as follows:
A-B + H2O → A-OH + B-H
In this reaction, "A-B" represents the substrate molecule, which is cleaved into two products (A-OH and B-H) through the addition of a water molecule. The versatility of hydrolases allows them to participate in numerous biochemical pathways, making them essential for life.
Classification of Hydrolases
Hydrolases are divided into several subclasses based on the type of chemical bond they act on. The major subclasses include:
Esterase
Esterases catalyze the hydrolysis of ester bonds, converting esters to acids and alcohols. These enzymes are involved in the breakdown of dietary fats, the regulation of neurotransmitters, and the detoxification of drugs and xenobiotics (e.g., native Schizophyllum commune cholesterol esterase). Esterases are used in the pharmaceutical industry for drug development, in the food industry for flavor enhancement, and in environmental biotechnology for biodegradation of contaminants.
Lipase
Lipases are a subclass of esterases that specifically catalyze the hydrolysis of triglycerides to glycerol and free fatty acids (e.g., native Streptomyces violaceoruber phospholipase A2, native Bacillus cereus phospholipase C). These enzymes play a critical role in lipid metabolism, including the digestion, absorption, and transport of dietary fats. Lipases are used in the production of biodiesel, the synthesis of enantiopure pharmaceuticals, and the processing of dairy and bakery products.
Glycosidase
Glycosidases, also known as glycosyl hydrolases, catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates, breaking down complex sugars into simpler sugars (e.g., oligoxyloglucan β-glycosidase, recombinant Streptococcus pyogenes endoglycosidase S). These enzymes are essential for the digestion of dietary carbohydrates, the biosynthesis of glycoconjugates, and the modification of glycoproteins. Glycosidases are used in the food and beverage industry to produce sweeteners, in the pharmaceutical industry for the synthesis of drugs, and in biotechnology for the analysis of glycan structures.
Peptidase
Peptidases, also known as proteases, catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in proteins and peptides, breaking them down into smaller peptides or individual amino acids (e.g., human endogenous retrovirus K endopeptidase, native Thermococcus thioreducens pyroglutamate aminopeptidase). These enzymes are essential for protein digestion, cellular regulation, and the activation of signaling pathways. Peptidases are widely used in the food industry for protein processing, in the pharmaceutical industry for the development of enzyme-based drugs, and in research for protein analysis.
Nuclease
Nucleases catalyze the hydrolysis of phosphodiester bonds in nucleic acids, resulting in the cleavage of DNA or RNA into smaller fragments (e.g., type III site-specific deoxyribonuclease, native bovine ribonuclease). These enzymes are critical for nucleic acid metabolism, including DNA replication, repair, recombination, and RNA processing. Nucleases are used in molecular biology for DNA cloning, sequencing and gene editing. They are also used in diagnostic assays and in the development of gene therapies.
Phosphatase
Phosphatases catalyze the hydrolysis of phosphate esters, removing phosphate groups from proteins, nucleotides, and other molecules (e.g., phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate 3-phosphatase). These enzymes are involved in signal transduction, energy metabolism, and the regulation of cellular processes. Phosphatases are used in research to study phosphorylation signaling pathways, in clinical diagnostics as biomarkers for various diseases, and in the development of treatments for metabolic disorders.
Applications of Hydrolases in Research and Industry
Hydrolases are invaluable tools in both research and industry due to their wide range of applications in various fields.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Hydrolases play a critical role in drug development and manufacturing:
- Drug Metabolism: Esterases and proteases are involved in the metabolism of prodrugs, converting them into their active forms. This property is exploited in the design of enzyme-activated drugs.
- Enzyme Therapy: Hydrolases, such as proteases and lipases, are used in enzyme replacement therapies for diseases such as cystic fibrosis and Gaucher's disease. These therapies involve the administration of specific enzymes to compensate for deficient or missing enzyme activity in patients.
- Biocatalysis: Hydrolases are used as biocatalysts in the synthesis of chiral drug intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Lipases, in particular, are used for the enantioselective synthesis of chiral compounds that are important for the production of certain drugs.
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology
Hydrolases are essential tools in molecular biology and biotechnology:
- DNA Manipulation: Nucleases, such as restriction enzymes, are used to cleave DNA at specific sequences to allow cloning and manipulation of genes. These enzymes are fundamental to recombinant DNA technology, gene editing and the development of genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- Protein Engineering: Proteases are used to selectively cleave proteins at specific sites, aiding in the purification and analysis of recombinant proteins. This application is important in the production of therapeutic proteins and in structural biology research.
- Enzymatic Assays: Hydrolases are used in various enzymatic assays to detect the presence or activity of specific biomolecules. For example, phosphatases are used in colorimetric assays to measure enzyme activity in biological samples.
Environmental Biotechnology
Hydrolases have significant applications in environmental protection and sustainability:
- Biodegradation: Hydrolases, such as lipases and esterases, are used in the biodegradation of environmental pollutants, including oils, plastics, and pesticides. These enzymes help break down complex pollutants into simpler, less toxic compounds that can be further degraded by microorganisms.
- Wastewater Treatment: Proteases and lipases are used in the treatment of industrial wastewater to break down organic contaminants, including proteins and fats. This process reduces the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) of the wastewater, making it safer for release into the environment.
- Biodiesel Production: Lipases are used in the transesterification of triglycerides to produce biodiesel. This process converts vegetable oils or animal fats into fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs), which are used as renewable biofuels.
Food and Beverage Industry
Hydrolases are widely used in the production and processing of food and beverages:
- Flavor Enhancement: Esterases and glycosidases are used to enhance flavor in foods by releasing aromatic compounds from precursors. For example, esterases are used to produce fruity flavors in beverages, while glycosidases can enhance the sweetness of low-calorie foods.
- Protein Hydrolysis: Proteases are used to hydrolyze proteins in dairy, meat and plant products to improve their texture, digestibility and nutritional value. They are also used in the production of protein hydrolysates, which are used as flavor enhancers and nutritional supplements.
- Lipid Processing: Lipases are used to modify fats and oils to produce structured lipids with specific properties, such as reduced trans-fat content. These enzymes are used in the production of margarine, low-fat spreads and other processed foods.
Industrial Applications
Hydrolases have broad industrial applications, contributing to the production of various commercial products:
- Detergents: Proteases and lipases are commonly used in laundry and dishwashing detergents to break down protein- and fat-based stains and increase cleaning efficiency. These enzymes are also used in enzyme-based industrial and household cleaners.
- Textile Processing: Hydrolases, such as cellulases and pectinases, are used in textile processing to improve fabric quality and texture. Cellulases are used to biopolish cotton fabrics, while pectinases are used to remove pectic substances from plant fibers during fabric production.
- Leather Processing: Proteases and lipases are used in the leather industry to remove hair, fat and other unwanted components from animal hides, thereby improving the quality and durability of finished leather products.

Hydrolases are a versatile and essential class of enzymes that play a critical role in various biological processes and have numerous applications in research and industry. Their ability to catalyze the hydrolysis of a wide range of chemical bonds makes them invaluable tools in fields such as pharmaceuticals, food production, environmental biotechnology, molecular biology, and industrial manufacturing. As an industry leader, Creative Enzymes offers the highest quality and most diverse selection of enzymes. Feel free to explore our offerings and don't hesitate to contact us with any questions.