Our Products Cannot Be Used As Medicines Directly For Personal Use.


Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Inhibitors
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that suppress or stop the activity of enzymes, biological catalysts that catalyze biological reactions. Enzyme inhibition regulates metabolic pathways in cells, maintaining balance and preventing excessive activity in certain pathways. In addition to their role in nature, enzyme inhibitors are of great interest in research, biotechnology and medicine, where they serve as valuable tools for therapeutic intervention, molecular research and industrial applications.
Creative Enzymes offers a wide range of premium enzyme inhibitors, carefully selected for quality and efficacy, to meet your research and development needs.
Mechanisms of Enzyme Inhibition
Enzyme inhibition occurs when an inhibitor binds to an enzyme and reduces its catalytic activity. What is inhibited varies from inhibitor to inhibitor and from binding site to binding site. Enzyme inhibition can generally be divided into two broad types: reversible and irreversible inhibition. Reversible inhibition can be further classified into competitive, non-competitive, and uncompetitive inhibition.
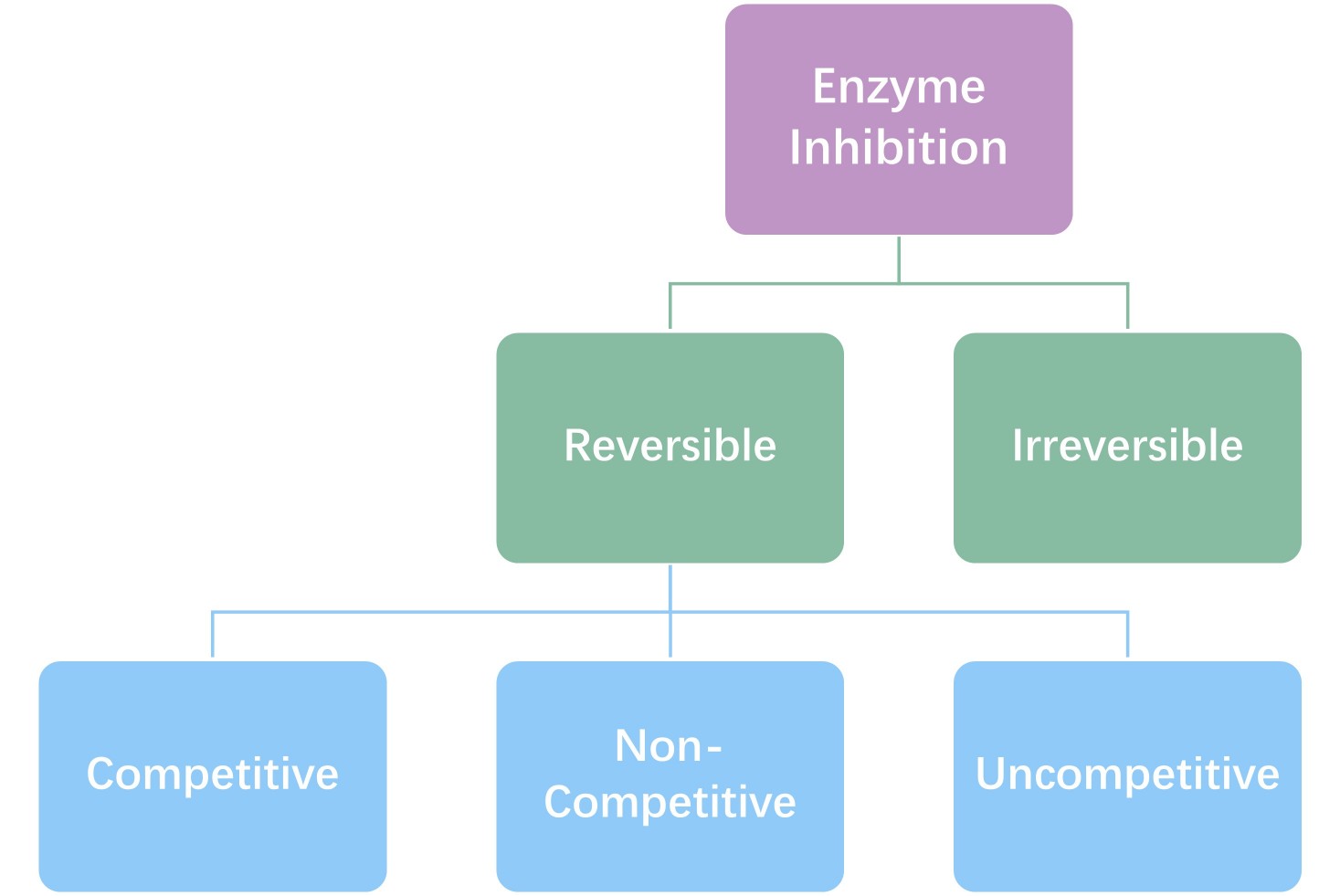 Fig. 1: Classification of enzyme inhibition.
Fig. 1: Classification of enzyme inhibition.
Reversible Inhibition
Reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently to enzymes, which means that their effect can be reversed. This can be done by removing the inhibitor or by adding more substrate. This type of inhibition is common in metabolic processes where enzymes need to be flexible and adapt as needed. There are three main types of reversible inhibition:
- Competitive inhibition occurs when an inhibitor and a substrate both tend to bind to the enzyme in an exclusive manner. The inhibitor is a compound that closely resembles the substrate, so it competes for the active site of the enzyme. When the inhibitor binds, it forms strong interactions with the enzyme, but no reaction occurs because the inhibitor can't react like the substrate. This "blocks" the enzyme, preventing the substrate from reacting and slowing the rate of the reaction. However, this type of inhibition is usually temporary and reversible. The degree of inhibition depends on how much substrate and inhibitor are present and how strongly each binds to the active site, since they're both competing for the same site.
- Non-competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the active site is occupied by the substrate. In fact, the enzyme can form complexes with both the substrate and the inhibitor at the same time. A common type of non-competitive inhibition is called allosteric inhibition. In this case, the inhibitor binds to another part of the enzyme, not the active site. This binding changes the shape of the enzyme so that it can no longer carry out its reaction.
- Uncompetitive inhibition is not common. In this case, the inhibitor binds to the enzyme and enhances the binding affinity of the substrate. However, although the enzyme-substrate-inhibitor complex is formed, the reaction is much slower. It's important to note that uncompetitive inhibition occurs after the enzyme has already bound to the substrate. This is different from non-competitive inhibition, which can occur whether or not the substrate is bound to the enzyme.
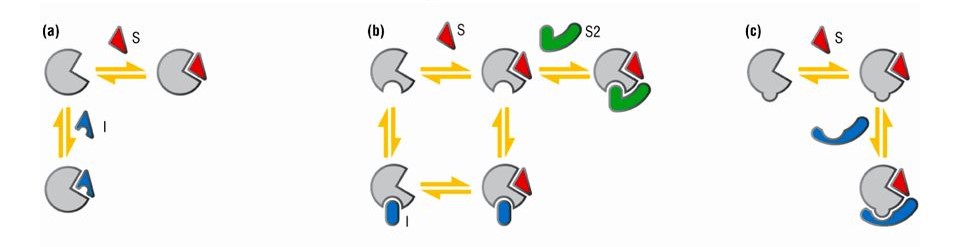 Fig. 2: Competitive, non-competitive and uncompetitive inhibition.
Fig. 2: Competitive, non-competitive and uncompetitive inhibition.
Irreversible Inhibition
In irreversible inhibition, the inhibitor covalently binds to the enzyme and permanently blocks its activity. Irreversible inhibitors usually target critical amino acid residues in the active site, making it impossible for the enzyme to function even if the inhibitor is removed. Examples include toxins and certain drugs, such as aspirin, which irreversibly inhibits the enzyme cyclooxygenase (recombinant human cyclooxygenase 1), to reduce inflammation.
Application of the Enzyme Inhibitors
Enzyme inhibitors play diverse and critical roles in both research and industrial applications. Some of the primary applications include:
Agricultural Applications
Enzyme inhibitors are used in agriculture to control pests and pathogens. Certain herbicides act as enzyme inhibitors by targeting enzymes that are critical for plant growth. For example, glyphosate, a widely used herbicide, inhibits an enzyme essential for amino acid synthesis in plants, thereby preventing their growth.
Research and Diagnostics
Enzyme inhibitors are essential tools in molecular biology research and diagnostics. Researchers use inhibitors to study enzyme pathways, determine enzyme specificity and analyze metabolic networks. In diagnostics, enzyme inhibitors are used in assay development, allowing scientists to quantify enzyme activity or assess inhibitor efficacy.
Industrial Applications
Enzyme inhibitors are used in industries such as food and beverage, textiles and biofuels, where specific enzymes need to be controlled to improve product quality and stability. In the brewing industry, for example, inhibitors of certain proteases help stabilize foam and extend the shelf life of beer.
 Fig. 3: Example of an enzyme inhibitor: tipranavir—an HIV protease inhibitor.
Fig. 3: Example of an enzyme inhibitor: tipranavir—an HIV protease inhibitor.
Creative Enzymes is pleased to supply various enzyme inhibitors of premium quality to the customers. We continue to be the most reliable supplier of enzyme products in the global market. Our prompt service, dedicated customer care, and reliable approach have made us the most preferred supplier. Contact us today to find the perfect Enzyme Inhibitors solution for your needs!
References:
- Geronikaki A, Eleutheriou PT. Enzymes and enzyme inhibitors—applications in medicine and diagnosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023;24(6):5245.
- Molecular biology of the cell (6th edition, 2015). Garland Science, Taylor and Francis group.
| Catalog | Product Name | EC No. | CAS No. | Source | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEI-0615 | IWP-3 | 687561-60-0 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0614 | Gö 6976 | 136194-77-9 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0613 | IBMX | 28822-58-4 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0612 | Calyculin A | 101932-71-2 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0611 | Okadaic acid | 78111-17-8 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0610 | Mifepristone | 84371-65-3 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0609 | RO 20-1724 | 29925-17-5 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0608 | Zaprinast | 37762-06-4 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0607 | T0070907 | 313516-66-4 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0606 | DPQ | 129075-73-6 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0605 | DR2313 | 284028-90-6 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0604 | NU 1025 | 90417-38-2 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0603 | MDBN | 1485-00-3 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0602 | DBeQ | 177355-84-9 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0601 | Pifithrin-α, Cyclic, hydrobromide | 511296-88-1 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0600 | Pifithrin-α | 63208-82-2 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0599 | C646, p300/CBP Inhibitor | 328968-36-1 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0598 | Garcinol | 78824-30-3 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0597 | Anacardic Acid | 16611-84-0 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0596 | CID 2745687 | 264233-05-8 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0595 | IWP-2 | 686770-61-6 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0594 | ML130 | 799264-47-4 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0593 | L-NMMA acetate | 53308-83-1 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0592 | L-NAME hydrochloride | 51298-62-5 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0591 | FK-866 | 658084-64-1 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0590 | BAY 11-7082 | 19542-67-7 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0589 | Rocaglamide | 84573-16-0 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0588 | Triptolide | 38748-32-2 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0587 | Sauchinone | 177931-17-8 | Inquiry | ||
| CEI-0586 | PDTC | 5108-96-3 | Inquiry |