Ribonuclease
Ribonuclease (RNase) is a class of enzymes that catalyze the degradation of RNA into smaller components. These enzymes, essential to various biological processes, transcend the laboratory environment by playing pivotal roles in numerous biological contexts, including viral defense mechanisms, cellular RNA turnover, and the processing of RNA precursors. In this article, we delve into the intricate world of ribonucleases, highlighting their structure, function, applications, and the vital contributions of Creative Enzymes in advancing RNase research.
Structure and Function of RNase
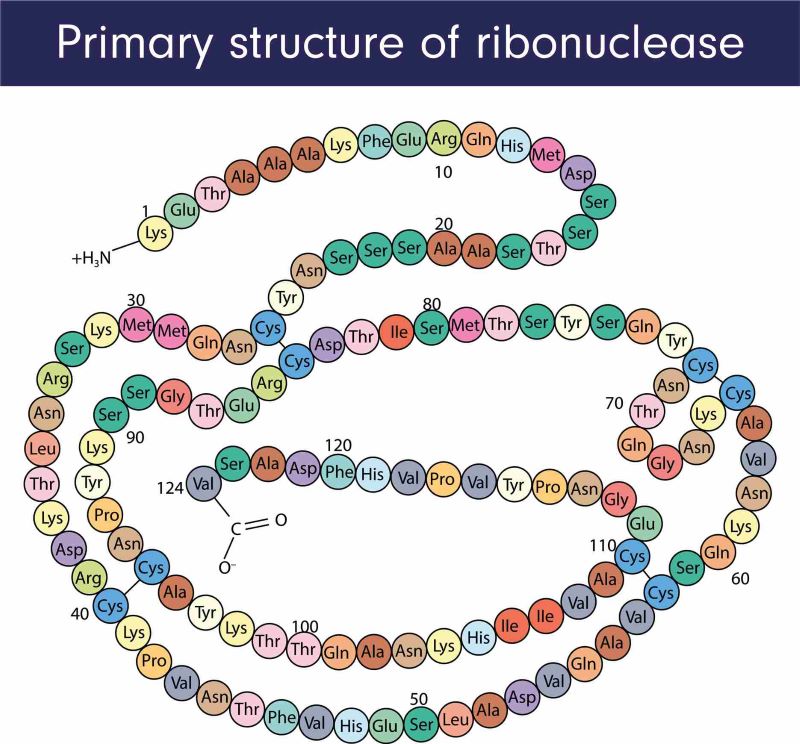
Ribonucleases are ubiquitous enzymes found in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans. These enzymes share a common function: the endonucleolytic cleavage of RNA, facilitated through several mechanisms, most notably hydrolysis. RNases exhibit remarkable diversity in their structure and mode of action. For example, RNase A, one of the most extensively studied ribonucleases, consists of a single polypeptide chain with four disulfide bonds, which confer stability and aid in its function.
RNases are classified into various families, including RNase A, RNase T1, RNase H, and RNase P, each with specific substrate preferences and catalytic mechanisms. For instance, RNase A preferentially cleaves the phosphodiester bonds at the 3' side of pyrimidine nucleotides, whereas RNase H specifically degrades the RNA strand of RNA-DNA hybrids.
Physiological and Biochemical Roles
The physiological roles of RNases are multifaceted. They participate in RNA processing, degradation, and regulation within the cell. RNase III, for example, is involved in the maturation of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and the processing of small regulatory RNAs. RNase P is essential for tRNA maturation, cleaving precursor tRNA molecules to generate mature tRNAs crucial for protein synthesis.
Moreover, RNases also play a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis by regulating RNA turnover. By degrading unnecessary or damaged RNAs, RNases prevent the accumulation of potentially harmful RNA molecules, thus ensuring cellular integrity.
Applications in Research and Biotechnology

The versatility of RNases has catalyzed their widespread application in research and biotechnology. In molecular biology, RNases are invaluable tools for RNA manipulation, including RNA sequencing, RNA splicing studies, and the generation of RNA fragments for further analysis. Techniques such as RNase protection assays, which leverage the specificity of RNases to detect and quantify RNA molecules, have become integral to gene expression studies.
Furthermore, RNases have emerged as potent anticancer agents. RNase-based therapeutics, such as ONCONASE® (ranpirnase), exploit the cytotoxic properties of RNases to selectively target and degrade RNA within cancer cells, inducing apoptosis and inhibiting tumor growth. This burgeoning field underscores the therapeutic potential of RNases.
Contribution of Creative Enzymes
Creative Enzymes stands at the forefront of enzyme innovation, providing a comprehensive suite of RNase products and services to support cutting-edge research and industrial applications. With a commitment to quality and scientific excellence, Creative Enzymes offers an extensive catalog of recombinant and native RNases, encompassing various specificities and catalytic properties.
One of the standout offerings from Creative Enzymes is their highly purified RNase A. Renowned for its stability and efficacy, RNase A from Creative Enzymes is meticulously produced to ensure optimal performance in a range of applications, from RNA isolation to molecular diagnostics.
In addition to product offerings, Creative Enzymes provides bespoke enzyme engineering services, enabling researchers to custom-design RNases tailored to their specific needs. Whether it's enhancing substrate specificity, altering catalytic activity, or optimizing stability, the expert team at Creative Enzymes leverages advanced techniques in protein engineering to meet the unique demands of their clients.
Moreover, Creative Enzymes' state-of-the-art analytical services offer comprehensive characterizations of RNase activity, providing valuable insights into enzyme kinetics, substrate interactions, and inhibition profiles. These services are indispensable for researchers seeking to elucidate the functional properties of RNases and their potential applications.
Ribonucleases, with their intricate structures and vital biological roles, are indispensable to both fundamental research and practical applications. The commitment of Creative Enzymes to providing top-tier RNase products and services empowers scientists and industries to harness the full potential of these remarkable enzymes. As our understanding of RNases continues to evolve, Creative Enzymes will undoubtedly remain a pivotal partner in advancing scientific discovery and biotechnological innovation. Whether in the quest to unravel the mysteries of RNA dynamics or in the pursuit of novel therapeutic interventions, Creative Enzymes is at the vanguard, catalyzing progress one enzyme at a time.