Our Products Cannot Be Used As Medicines Directly For Personal Use.


Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Substrates
In biochemistry, substrates are molecules that are targeted by enzymes. They participate in enzyme reactions and are converted or degraded into other molecules. The substrates bind to the site of enzyme activity and form the enzyme-substrate complex. After being converted into products, the substrates are released from the enzymes.
Creative Enzymes offers high purity substrates in variable quantities to meet all your needs. These substrates cover most areas of industrial production and research. Our substrate products include small molecule substrates, peptide & protein substrates, saccharide substrates, and chromogenic & fluorogenic substrates.
Definition of Substrates
A substrate is defined as the molecule on which an enzyme acts. In the case of enzymes and substrates, molecular complementarity governs the interaction: specific structural features of the enzyme bind to complementary features on the substrate, often through the active site of the enzyme. When a substrate binds to an enzyme, it forms an enzyme-substrate complex that undergoes a catalytic reaction that converts the substrate into products. The enzyme itself is not altered in the reaction, so it can catalyze many substrate molecules in sequence.
The specificity of the enzyme-substrate interaction is remarkable. Factors such as shape, charge, and hydrophobic/hydrophilic properties all play a role in determining this fit. The enzyme's active site is finely tuned to recognize and bind specific substrates, ensuring that each enzyme catalyzes only particular reactions. This specificity is critical to making biological processes work.
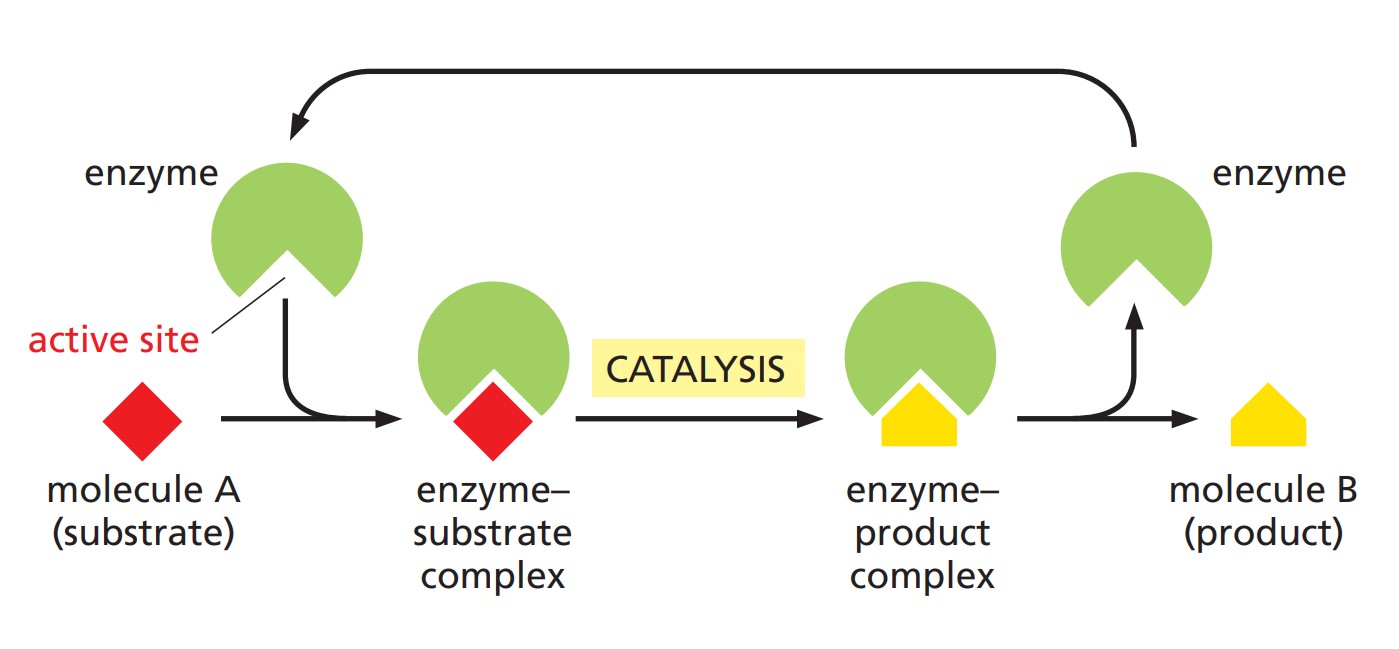 Fig. 1: How enzymes work. each enzyme has an active site to which one or more substrate molecules bind, forming an enzyme–substrate complex. a reaction occurs at the active site, producing an enzyme–product complex. The product is then released, allowing the enzyme to bind further substrate molecules (Molecular Biology of the Cell, 6th Edition).
Fig. 1: How enzymes work. each enzyme has an active site to which one or more substrate molecules bind, forming an enzyme–substrate complex. a reaction occurs at the active site, producing an enzyme–product complex. The product is then released, allowing the enzyme to bind further substrate molecules (Molecular Biology of the Cell, 6th Edition).
Reaction Mechanisms of Enzyme-Substrate Complexes
The reaction mechanisms by which enzymes catalyze the conversion of substrates are complex and involve multiple steps. These mechanisms can be broadly categorized based on the induced fit model and the lock-and-key model.
Lock-and-Key Model
In this model, the active site of the enzyme is precisely shaped to fit a specific substrate, like a lock and key. The enzyme-substrate complex can only bind to substrates of the correct shape and chemical nature. Once bound, the reaction proceeds without major structural changes to the enzyme.
Induced Fit Model
According to this model, when the substrate binds, the enzyme conforms to fit the substrate. This flexibility allows the enzyme to exert specific forces on the substrate to maintain the transition state and lower the activation energy of the reaction. The induced-fit model is widely accepted because it accounts for the dynamic nature of enzyme-substrate interactions and their high specificity and efficiency.
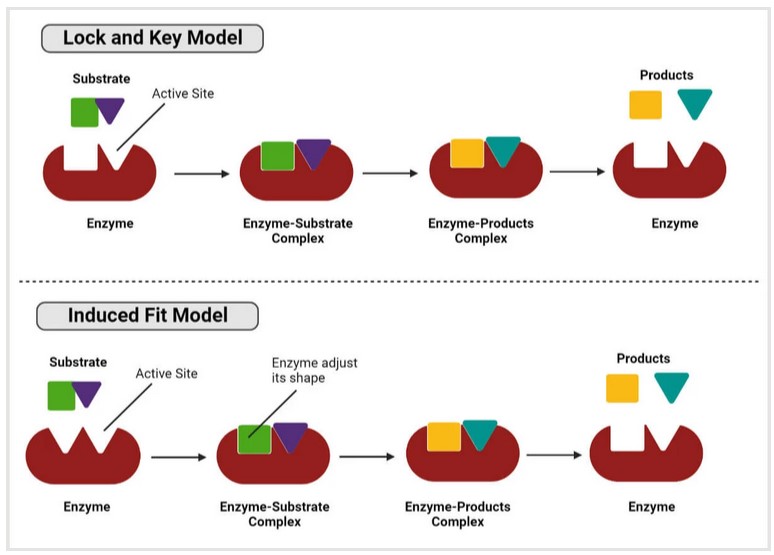 Fig. 2: Lock and key model and induced fit model.
Fig. 2: Lock and key model and induced fit model.
During an enzymatic reaction, there is a transition state-an intermediate configuration in which the substrate is prepared for conversion to the product. Enzymes achieve this by stabilizing the transition state through various mechanisms. For example, enzymes bring substrate molecules closer together (proximity effects) and align them perfectly for the reaction to occur (orientation effects). They can also donate or accept protons to aid the process (acid-base catalysis), form temporary bonds with substrates (covalent catalysis), or stabilize charged regions within the active site (electrostatic catalysis). By combining these strategies, enzymes lower the energy barrier required for reactions. This allows them to operate rapidly and efficiently, even under the mild conditions found in living organisms.
Types of Enzyme Substrates
Enzyme substrates can be categorized based on several factors, including chemical nature, reactivity, and the types of bonds involved in enzyme catalysis. Here are the major types:
Universal vs. Specific Substrates
- Universal substrates are molecules that can be targeted by many enzymes, even from different species or metabolic pathways. These substrates have a general structure or functional group that most enzymes can recognize, allowing different enzymes to react with them. Examples include ATP and NADH.
- Specific substrates are molecules that a particular enzyme can recognize and act on, often with high specificity. These substrates have a unique structure or functional group that aligns precisely with the enzyme's active site, and the enzyme is highly selective for that substrate alone. Specific substrates are features of enzymes that catalyze precise reactions in well-defined biochemical pathways, where specificity allows for tight regulation.
Competitive and Non-Competitive Substrates
- Competitive substrates bind to the site of enzyme action and compete with other molecules or inhibitors for the enzyme. Researchers often use competitive substrates to study enzyme inhibition, where an inhibitor competes with the substrate for binding and reduces the reaction rate.
- Non-competitive substrates bind to sites other than the active site of the enzyme and change the conformation of the enzyme, but do not inhibit the active site. Noncompetitive substrate behavior occurs when enzymes have multiple binding sites or can catalyze reactions with multiple substrates simultaneously.
Primary vs. Secondary Substrates
- Primary substrates are the main molecules that undergo transformation by an enzyme. They are directly involved in the reaction and are converted into products.
- Secondary substrates are added to the reaction but are not converted into products. Instead, they can serve as cofactors or cosubstrates, providing additional molecules or ions needed for enzymatic activity. For example, ATP can be a secondary substrate for kinases by accepting a phosphate atom to be transferred to a primary substrate.
Covalent vs. Non-covalent Substrates
- Covalent substrates are those that temporarily form covalent bonds with the enzyme during the reaction. This covalent attachment facilitates the formation of transition states and the overall reaction process.
- Non-covalent substrates bind to the enzyme through weak interactions like hydrogen bonding, ionic bonds, or van der Waals forces, which are reversible interactions that often result in product without forming a covalent bond with the enzyme.
Our Diverse Range of Substrates Products
Creative Enzymes provides high-purity substrates available in various quantities to suit diverse requirements. These substrates support a wide range of applications, from industrial production to exploratory research. Our product offerings include:
Small Molecule Substrates
There are thousands of enzyme substrates in small molecules. They participate in reactions such as dehydrogenation, decarboxylation, transamination, and isomerization. Our chemical substrates fuel most biochemical reactions. We supply not only standard substrates such as esterase substrates, HRP (horseradish peroxidase substrates), phosphatase substrates, sulfatase substrates, but also some specialty substrates. The variety is there to meet all your needs.
Peptide & Protein Substrates
Proteases catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, a process that breaks down proteins into smaller polypeptide chains or amino acids. These enzymes are essential in various biological and industrial processes, including protein digestion, cell signaling, and biotechnology applications. To support your research and experiments, we offer a comprehensive selection of substrates, including high-quality native protein substrates and synthetic polypeptide substrates. Our products are designed to provide reliable and accurate results in a wide range of applications.
Saccharide Substrates
Saccharides (also known as sugars or carbohydrates) are common substrates for the biochemical industry. We offer polysaccharides, oligosaccharides and monosaccharides for various purposes. For example, soluble starch, amylopectin (amylopectin azure), and amylose substrates for amylase assays, and many monosaccharides and disaccharides are ideal for isomerase assays.
Chromogenic & Fluorogenic Substrates
These substrates produce visible or fluorescent light when they interact with specific enzymes. They are widely used in ELISAs and other activity assays, especially when working with low enzyme concentrations—they provide highly sensitive detection. For example, p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) is commonly used as a chromogenic substrate for phosphatases (4-nitrophenyl phosphate disodium salt hexahydrate), while fluorescein diphosphate (FDP) is ideal for alkaline phosphatase. Our chromogenic and fluorogenic substrates are designed to provide reliable and accurate results, making them an excellent choice for a wide range of research applications.
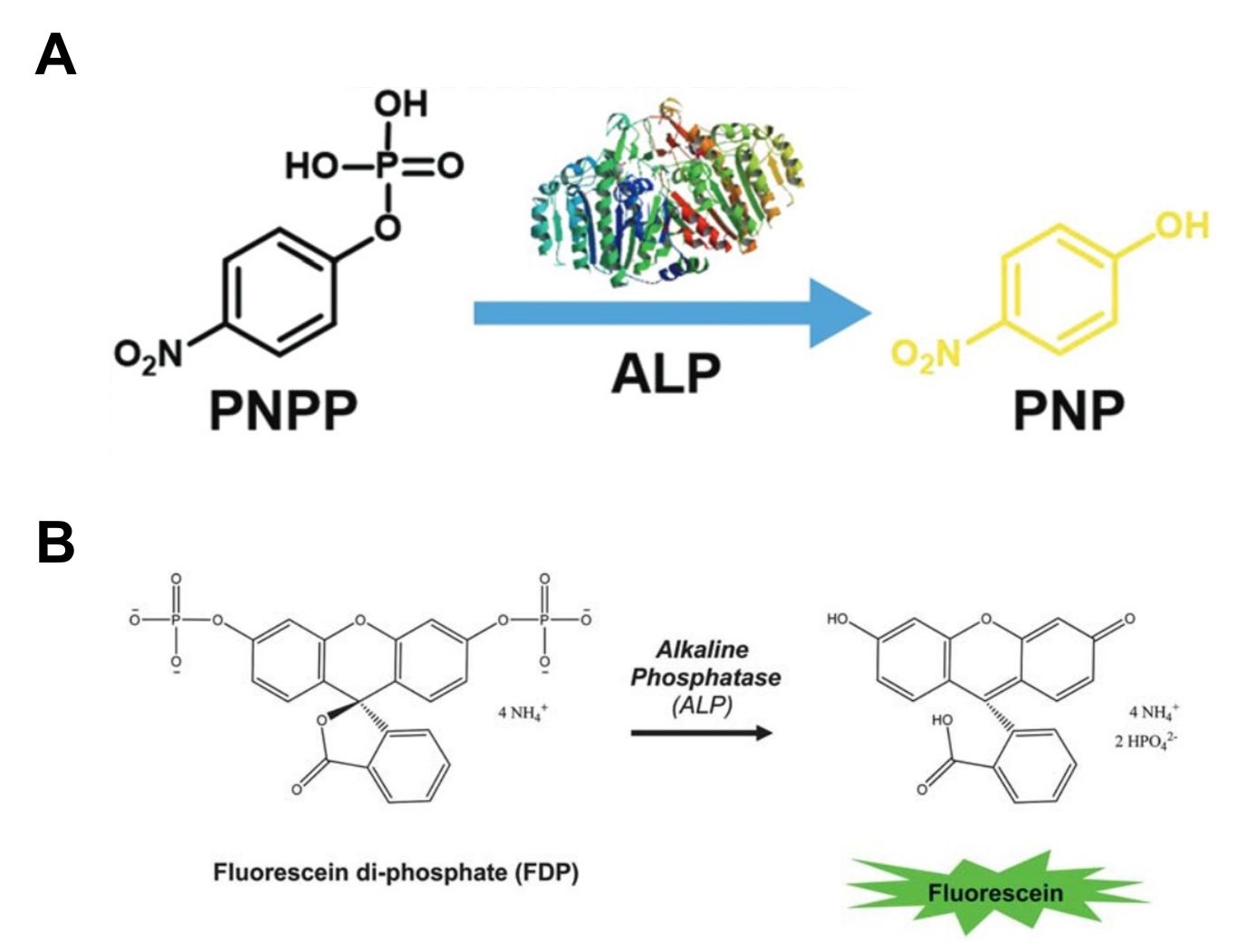 Fig. 3: Examples of chromogenic and fluorogenic substrate. A. p-nitrophenylphosphate (PNPP) can be catalytically converted to p-nitrophenol (PNP) (slight yellow) by alkaline phosphatase (Zhang et al., 2017). B. Scheme of the biocatalytic reaction triggered by alkaline phosphatase leading to dephosphorylation of fluorescein diphosphate and subsequent fluorescein production (Mertz et al., 2011).
Fig. 3: Examples of chromogenic and fluorogenic substrate. A. p-nitrophenylphosphate (PNPP) can be catalytically converted to p-nitrophenol (PNP) (slight yellow) by alkaline phosphatase (Zhang et al., 2017). B. Scheme of the biocatalytic reaction triggered by alkaline phosphatase leading to dephosphorylation of fluorescein diphosphate and subsequent fluorescein production (Mertz et al., 2011).
Creative Enzymes specializes in the enzyme industry. We are proud to offer all types of products and services related to enzymes, especially enzyme substrates. Creative Enzymes guarantees high purity enzyme substrate products that are manufactured under quality assurance and certified by HPLC or other fine analytical methods. We also supply substrates in various degrees of purity and specifications to meet different requirements. These substrates can be used in many aspects of enzyme activity measurement or production practices. Contact us today to find the perfect substrate solution for your needs!
References:
- Mertz D, Vogt C, Hemmerlé J, et al. Tailored design of mechanically sensitive biocatalytic assemblies based on polyelectrolyte multilayers. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(23):8324.
- Zhang J, Lu X, Lei Y, Hou X, Wu P. Exploring the tunable excitation of QDs to maximize the overlap with the absorber for inner filter effect-based phosphorescence sensing of alkaline phosphatase. Nanoscale. 2017;9(40):15606-15611.