Our Products Cannot Be Used As Medicines Directly For Personal Use.


Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Lyases
Lyases are a class of enzymes that play a vital role in various biochemical processes by catalyzing the addition or removal of chemical groups in molecules, often resulting in the formation of double bonds or the cleavage of single bonds without hydrolysis or oxidation. These enzymes are essential for many metabolic pathways and have a wide range of applications in research and industry. Understanding the function and potential uses of lyases is critical to the advancement of several fields, including biotechnology, medicine, and environmental science. As an industry-leading supplier of enzymes, Creative Enzymes is pleased to offer a comprehensive range of high-quality lyases, with approximately 150 varieties, tailored to meet the diverse requirements of our customers.
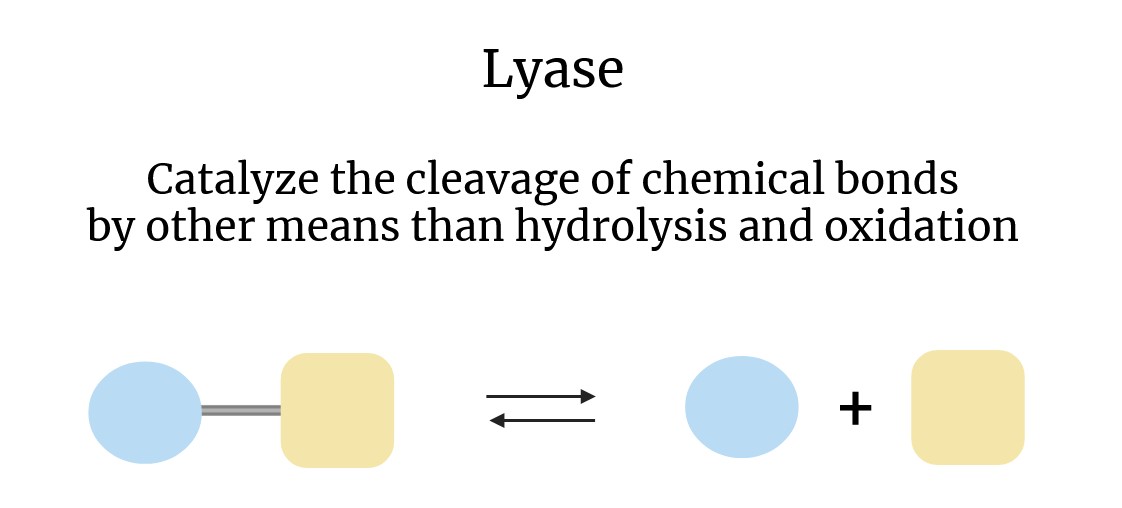
Lyases are classified under EC (Enzyme Commission) number 4, which defines them as enzymes that facilitate the cleavage of bonds through mechanisms other than hydrolysis or oxidation. This process typically results in the formation of a new double bond or a new ring structure. In contrast to hydrolases, which break bonds using water, or oxidoreductases, which involve the transfer of electrons, lyases frequently remove groups from their substrates, leaving behind a double bond or, conversely, adding groups to a double bond.
The general reaction catalyzed by lyases can be represented as follows:
A-B → A + B
or
A + B → A-B
In this reaction, "A-B" represents the substrate molecule, which is either broken down into two products (A and B) or synthesized from two smaller molecules (A and B).
Classification of Lyases
Lyases are classified into several subclasses based on the type of chemical bond they act upon. The major subclasses include:
Carbon-Carbon Lyase
Carbon-carbon lyases catalyze the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds in a substrate. They are involved in a variety of metabolic processes, including the breakdown and synthesis of complex organic molecules. Decarboxylation reactions in which a carboxyl group is removed from a substrate, resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide and a new compound. A notable example is aldolase (e.g., 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-pentonate aldolase), which in glycolysis catalyzes the readily reversible splitting of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (F-1,6-BP) into the products glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP). Carbon-carbon lyases are used in the synthesis of fine chemicals and pharmaceuticals, and in metabolic engineering to produce biofuels and other valuable compounds.
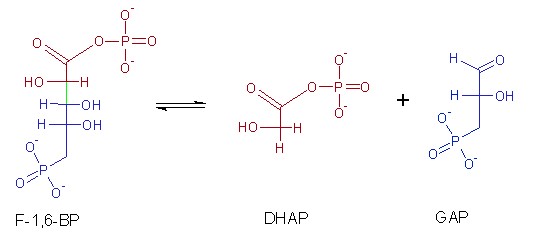 Fig. 1: The reaction that takes place in the second stage of glycolysis and catalyzed by aldolase.
Fig. 1: The reaction that takes place in the second stage of glycolysis and catalyzed by aldolase.
Carbon-Oxygen Lyase
Carbon-oxygen lyases catalyze the cleavage of carbon-oxygen bonds, often resulting in the formation of a new double bond or the addition of water to a double bond. An example is the dehydration of alcohols to alkenes or the hydration of alkenes to alcohols. Carbon-oxygen lyases are used in the food and beverage industry to produce flavors and aromas, and in the pharmaceutical industry for the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
Carbon-Nitrogen Lyase
Carbon-nitrogen lyases catalyze the cleavage of carbon-nitrogen bonds commonly found in amino acids and other nitrogen-containing compounds. For example, the deamination of amino acids, in which an amino group is removed, resulting in the formation of a keto acid and ammonia (e.g., glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase, aminodeoxyfutalosine deaminase). These enzymes are essential in the biosynthesis of amino acids, the degradation of nitrogenous compounds in wastewater treatment, and the development of diagnostic assays for various diseases.
Carbon-Sulfur Lyase
Carbon-sulfur lyases catalyze the cleavage of carbon-sulfur bonds that are important in the metabolism of sulfur-containing compounds. A notable example is the cleavage of cysteine to pyruvate, ammonia, and hydrogen sulfide (e.g., D-cysteine desulfhydrase). Carbon-sulfur lyases are used in the bioremediation of sulfur-containing pollutants, the synthesis of sulfur-containing drugs, and the production of sulfur-based chemicals.
Carbon-Halide Lyase
Carbon-halide lyases catalyze the cleavage of carbon-halide bonds found in halogenated organic compounds. The most common example is the dehalogenation of haloalkanes, resulting in the formation of alkanes and halide ions (e.g., haloalkane dehalogenase). These enzymes are used in the detoxification of halogenated environmental pollutants, the synthesis of halogen-free organic compounds, and the development of biocatalytic processes for the chemical industry.
Phosphorus-Oxygen Lyase
Phosphorus-oxygen lyases catalyze the cleavage of phosphorus-oxygen bonds that are critical in the metabolism of nucleotides and other phosphorus-containing compounds. The most important example in cellular processes is the cyclization of ATP to cyclic AMP (cAMP) and pyrophosphate. Phosphorus-oxygen lyases are important in the study of signal transduction pathways, the development of anticancer drugs, and the production of cyclic nucleotide derivatives for research and therapeutic purposes.
Applications of Lyases in Research and Industry
Lyases have a wide range of applications across various fields, making them invaluable tools in both research and industry.
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology
Lyases are essential tools in molecular biology and biotechnology:
- Gene Cloning and Expression: Lyases, such as DNA ligases, are used in gene cloning and expression studies. DNA ligases catalyze the formation of phosphodiester bonds between DNA fragments, allowing the insertion of genes into plasmids for expression in host cells.
- Protein Engineering: Lyases are used in the modification of proteins for research and industrial applications. For example, site-specific lyases are used to introduce specific mutations into proteins, allowing researchers to study protein structure and function.
- Metabolic Engineering: Lyases are used in the metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce valuable biochemicals such as amino acids, organic acids and antibiotics. By manipulating lyase activity, researchers can optimize metabolic pathways to increase the yield of desired products.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Lyases play a critical role in drug development and manufacturing:
- Drug Synthesis: Lyases are used in the synthesis of complex drug molecules, particularly those involving the formation or cleavage of carbon-carbon and carbon-nitrogen bonds. For example, carbon-carbon lyases are used in the manufacture of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and other therapeutic agents.
- Enzyme Therapy: Certain lyases are used in enzyme replacement therapies for metabolic disorders, such as phenylketonuria, in which patients lack certain enzymes required for normal metabolism. These therapies involve the administration of the missing enzyme to restore metabolic function.
- Biocatalysis: Lyases are employed as biocatalysts in the enantioselective synthesis of chiral drug intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Their ability to catalyze reactions under mild conditions makes them ideal for sustainable and green chemistry applications in the pharmaceutical industry.
Environmental Biotechnology
Lyases have significant applications in environmental protection and sustainability:
- Bioremediation: Lyases, particularly carbon halide lyases, are used in the bioremediation of halogenated organic contaminants such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and chlorinated solvents. These enzymes help break down these persistent environmental contaminants into less harmful compounds.
- Waste Treatment: Carbon-sulfur lyases are used in the treatment of industrial wastewater containing sulfur compounds. These enzymes help reduce the levels of sulfur-containing pollutants, such as hydrogen sulfide, which can be toxic to aquatic life and contribute to environmental pollution.
- Biofuel Production: Lyases are involved in the production of biofuels from renewable resources. For example, carbon-carbon lyases are used in the metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce biofuels, such as ethanol and butanol, from biomass.
Food and Beverage Industry
Lyases are widely used in the production and processing of food and beverages:
- Flavor and Aroma Production: Carbon-oxygen lyases are used to produce flavor and aroma compounds in food products. For example, pectin lyases are used in the fruit juice industry to break down pectin, resulting in clearer juices with enhanced flavors.
- Fermentation Processes: Lyases play a role in fermentation processes, where they are involved in the production of alcohols, acids, and other fermentation products. For example, pyruvate decarboxylase, a carbon-carbon lyase, is essential for the production of ethanol during alcoholic fermentation.
- Nutrient Enhancement: Certain lyases are used to improve the nutritional value of foods. For example, phytase, a phosphorus-oxygen lyase, is used to break down phytic acid in cereals and legumes, increasing the bioavailability of essential minerals such as calcium, iron and zinc.

Lyases are a diverse and versatile class of enzymes that play a critical role in various biological processes and have numerous applications in research and industry. Their ability to catalyze the addition or removal of chemical groups without hydrolysis or oxidation makes them invaluable tools in fields such as pharmaceuticals, food production, environmental biotechnology, and molecular biology. Creative Enzymes is a trusted leader in the supply of enzymes, offering a diverse range of high-quality products. Explore our complete product catalog or contact us for custom enzyme blends tailored to your needs.
| Catalog | Product Name | EC No. | CAS No. | Source | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATE-0049 | Native Spinach Aldolase | EC 4.1.2.13 | 9024-52-6 | Spinach | Inquiry |
| NATE-0048 | Native Rabbit Aldolase | EC 4.1.2.13 | 9024-52-6 | Rabbit muscle | Inquiry |
| NATE-0024 | Native Porcine Aconitase | EC 4.2.1.3 | 9024-25-3 | Porcine heart | Inquiry |
| NATE-0363 | Native E. coli 3-Deoxy-D-manno-octulosonate Aldolase | EC 4.1.2.23 | 9026-95-3 | E. coli | Inquiry |
| NATE-0098 | Carbonic Anhydrase II from Human, Recombinant | EC 4.2.1.1 | 9001-03-0 | E. coli | Inquiry |
| NATE-0097 | Native Human Carbonic Anhydrase I | EC 4.2.1.1 | 9001-03-0 | Human erythrocy... | Inquiry |
| DIA-272 | Native Cystathionine-β-synthase | EC 4.2.1.22 | 9023-99-8 | Inquiry | |
| DIA-225 | Native Human Neuron Specific Enolase | EC 4.2.1.11 | 9014-08-8 | Human brain | Inquiry |
| DIA-212 | Native Microorganism Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase | EC 4.1.1.31 | 9067-77-0 | Microorganism | Inquiry |
| DIA-182 | Native Microorganism N-Acetylneuraminic acid aldolase | EC 4.1.3.3 | 9027-60-5 | Microorganism | Inquiry |