
Fructus Gardeniae has been reported to exhibit functions of protecting the liver, gallbladder, reducing blood pressure, calming, stopping bleeding as well as swelling, and has been applied as a traditional medicine for the treatment of jaundice, fever, hypertension, contusion, diabetes, skin ulcers and other diseases. Fructus Gardeniae as the first batch of medicine and food resources promulgated by the Ministry of Health has been traditionally used for sprain in many Asian countries. Fructus Gardeniae contains saffron glycosides and thus can be used as a yellow edible dye.
Ingredient Overview
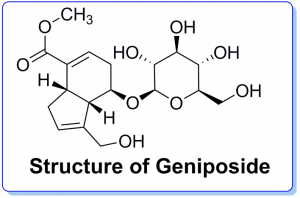 The main constituents of Fructus Gardeniae extract include iridoid glycosides and their aglycones, such as geniposide, gardenoside and genipin. Geniposide is one of the main components of Fructus Gardeniae. Many pharmacological studies have indicated that geniposide possesses diverse biological activities. Geniposide could be transformed into the blue pigments by some aerobic bacteria, signifying that geniposide is the precursor for the formation of pigments after converting into genipin by β-glucosidase. Crocin and its aglycone, crocetin, are also important components of this extract. Chlorogenic acid and ursolic acid also exist in Fructus Gardeniae extract.
The main constituents of Fructus Gardeniae extract include iridoid glycosides and their aglycones, such as geniposide, gardenoside and genipin. Geniposide is one of the main components of Fructus Gardeniae. Many pharmacological studies have indicated that geniposide possesses diverse biological activities. Geniposide could be transformed into the blue pigments by some aerobic bacteria, signifying that geniposide is the precursor for the formation of pigments after converting into genipin by β-glucosidase. Crocin and its aglycone, crocetin, are also important components of this extract. Chlorogenic acid and ursolic acid also exist in Fructus Gardeniae extract.
Pharmacokinetics of Geniposide
Geniposide is stable and shows no change in gastric juice at pH 1.8 at 37 °C, while it can be metabolized to genipin in the intestinal tract. Gardenoside is unstable to acid and heat. It can be converted into deacetylasperulosidic acid metbylester (DAM) and methyl sulphate (Scan-doside methylester, SSM) in gastric juice. In the intestinal tract, DAM would be converted to DAM-genin and SSM is converted to SSM-genin.
Pharmacological Action
- Impact on the digestive system
- Liver protection: Fructus Gardeniae can alleviate liver damage caused by CCl4, reduce degeneration and necrosis of hepatocytes, and recover glycogen and ribonucleic acid content in liver cells. Infusion of Fructus Gardeniae can reduce the activity of alanine aminotransferase and bilirubin diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase in the animals with a ligated common bile duct, or rises vitality of the supressed liver diphosphate-glucose dehydrogenase
- Effects on bile secretion, excretion and metabolism: Fructus Gardeniae has a choleretic effect. Its alcohol extract, saffron glucoside, saffron acid and genipo can increase bile secretion. People who take decoction of Fructus Gardeniae have an obvious gallbladder shrink and their bile excretion is promoted. Gardenia water and alcohol extract can reduce the content of bilirubin in the blood of rabbits with ligated common bile ducts, and it seems to promote the metabolism of bilirubin.
- Effects on gastric secretion and gastrointestinal motility: Geniposide in the duodenum can reduce the secretion of gastric juice in rats with pylorus ligation. Intravenous deoxyxanthin or genipoin can inhibit spontaneous gastric peristalsis and pilocarpine-induced gastric contraction in rats. The alcohol extract of Fructus Gardeniae can stimulate the movement of the small intestine of rats and rabbits.
- The role in the central nervous system
Intraperitoneal injection of Fructus Gardeniae alcohol extract in mice can reduce spontaneous activity through a sedative effect, and its synergistic effect with sodium hexabarbital can prolong sleep time and decrease body temperature. Gardenia water extract, deoxyxanthin and genipo can inhibit the acetic acid writhing reaction in mice, so it is considered to have an analgesic effect.
- The role in the cardiovascular system
Decoction and alcohol extract of Fructus Gardeniae have antihypertensive effects on anesthetized or non-anesthetized cats, rabbits, and rats, whether administered orally or intravenously. Fructus Gardeniae extract can reduce myocardial contractility, and its decoction has activity of slowing heart rate and expanding blood vessel.
- Anti-inflammatory effect
Fructus Gardeniae extract can significantly inhibit the swelling of mouse ear shell caused by xylene and the swelling of athlete’s foot caused by formaldehyde. At the same time, it has obvious therapeutic effects on soft tissue damage of mice and rabbits.
- Anti-bacterial effect
Fructus Gardeniae has inhibitory effects on Staphylococcus aureus, Meningococcus, and Catarrhalis. Fructus Gardeniae aqueous extract has an inhibitory effect on various fungi in vitro, and its decoction has the effect of killing Leptospira and adult Schistosoma.
- Other effects
Fructus Gardeniae extract can make the blood flow of pancreas, liver, stomach and small intestine rise, and the recovery of pancreatic blood flow is most obvious. Fructus Gardeniae can also slow down the interpretation process of ATP in red blood cells of mice, resulting in insufficient energy supply.
Tips
Fructus Gardeniae extract tastes bitter and its cold nature would hurt the stomach. Therefore, it is not suitable for people with spleen deficiency.
Related Product at Creative Enzymes:

Leave a Reply